| Citation: | Qixing Han, Lidong Zhou. ASYMPTOTIC PROPERTIES OF A STOCHASTIC ECO-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL MODEL WITH FEAR EFFECT AND HUNTING COOPERATION[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(4): 1975-1995. doi: 10.11948/20240374 |
ASYMPTOTIC PROPERTIES OF A STOCHASTIC ECO-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL MODEL WITH FEAR EFFECT AND HUNTING COOPERATION
-
Abstract
In this paper, we put forward and analyze a stochastic eco- epidemiological model with disease in the prey population, which incorporates fear effect of predators on prey and hunting cooperation among predators. We find out sufficient criteria for the existence and uniqueness of an ergodic stationary distribution of positive solutions to the system by using the stochastic Lyapunov function methods. Moreover, we also derive sufficient criteria for extinction of the infected prey population and the predator population. Additionally, we give the specific expression of the probability density function of the stochastic model near the unique endemic quasi-equilibrium by solving the Fokker-Planck equation. In the end, the supporting theoretical results are verified by numerical simulation.
-

-
References
[1] A. Ali, S. Khan, I. Ali and F. U. Khan, On dynamics of stochastic avian influenza model with asymptomatic carrier using spectral method, Math. Method. Appl. Sci., 2022, 45, 8230–8246. doi: 10.1002/mma.8183 [2] J. Chattopadhyay and O. Arino, A predator-prey model with disease in the prey, Nonlinear Anal., 1999, 36(6), 747–766. doi: 10.1016/S0362-546X(98)00126-6 [3] N. Dalal, D. Greenhalgh and X. Mao, A stochastic model for internal HIV dynamics, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2008, 341(2), 1084–1101. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2007.11.005 [4] H. Hethcote, W. Wang, L. Han and Z. Ma, A predator-prey model with infected prey, Theor. Popul. Biol., 2004, 66(3), 259–268. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2004.06.010 [5] D. Higham, An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations, SIAM Rev., 2001, 43(3), 525–546. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 [6] G. Hussain, A. Khan, M. Zahri and G. Zaman, Ergodicstationarydistribution ofstochastic epidemic model for HBV with double saturated incidence rates and vaccination, Chaos. Soliton. Fract., 2022, 160, 112195. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112195 [7] C. Ji, D. Jiang and N. Shi, Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-type II schemes with stochastic perturbation, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2009, 359(2), 482–498. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.05.039 [8] R. Khasminskii, Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, Springer Heidelberg Dordrecht London, New York, 2012. [9] Q. Liu, Dynamical analysis of a stochastic maize streak virus epidemic model with logarithmic Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process, J. Math. Biol., 2024, 89(3), 1–75. [10] Q. Liu and D. Jiang, Stationary distribution and probability density for a stochastic SEIR-type model of coronavirus COVID-19 with asymptomatic carriers, Chaos. Soliton. Fract., 2023, 169, 113256. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113256 [11] Q. Liu, D. Jiang, N. Shi, T. Hayat and B. Ahmad, Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SEIR epidemic model with standard incidence, Phys. A., 2017, 469, 510–517. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.11.077 [12] J. Liu, B. Liu, P. Lv and T. Zhang, An eco-epidemiological model with fear effect and hunting cooperation, Chaos. Soliton. Fract., 2020, 142, 110494. [13] K. Mamis and M. Farazmand, Stochastic compartmental models of COVID-19 pandemic must have temporally correlated uncertainties, Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys., 2023, 479, 20220568. [14] X. Mao, Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, Horwood Publishing, Chichester, 1997. [15] S. Meyn and R. Tweedie, Stability of Markovian processes III: Foster-Lyapunov criteria for continuous-time processes, Dav. Appl. Prob., 1993, 25, 518–548. [16] P. Panday, S. Samanta, N. Pal and J. Chattopadhyay, Delay induced multiple stability switch and chaos in a predator prey model with fear effect, Math. Comput. Simulat., 2019, 172, 134–158. [17] H. Qi, S. Zhang, X. Meng and H. Dong, Periodic solution and ergodic stationary distribution of two stochastic SIQS epidemic systems, Phys. A., 2018, 508, 223–241. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.05.075 [18] H. Roozen, An asymptotic solution to a two-dimensional exit problem arising in population dynamics, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1989, 49(6), 1793–1810. doi: 10.1137/0149110 [19] Y. Tan, Y. Cai, X. Sun, K. Wang, R. Yao, W. Wang and Z. Peng, A stochastic SICA model for HIV/AIDS transmission, Chaos. Soliton. Fract., 2022, 165, 112768. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112768 [20] E. Venturino, Epidemics in predator-prey models: Disease in the predators, IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol., 2002, 19(3), 185–205. doi: 10.1093/imammb/19.3.185 [21] J. Wang and S. Liu, Persistence and extinction of the tumor-immune stochastic model with effector cells and cytokines, J. Appl. Anal. Comput., 2020, 13, 655–670. [22] X. Wang, L. Zanette and X. Zou, Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions, J. Math. Biol., 2016, 73, 1179–1204. doi: 10.1007/s00285-016-0989-1 [23] Y. Xiao and L. Chen, Modelling and analysis of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey, Math. Biosci., 2001, 171(1), 59–82. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(01)00049-9 [24] Q. Zhang, D. Jiang, Z. Liu and D. O'Regan, Asymptotic behavior of a three species eco-epidemiological model perturbed by white noise, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2016, 433, 121–148. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.07.025 [25] B. Zhou, X. Zhang and D. Jiang, Dynamics and density function analysis of a stochastic SVI epidemic model with half saturated incidence rate, Chaos. Soliton. Fract., 2020, 137, 109865. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109865 -
-
-
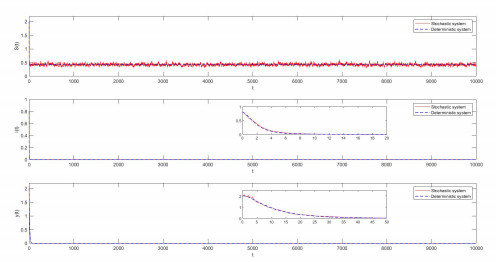
Figure 1.
The figure on the left shows the solution of stochastic system and deterministic system when
$ R_{p}^{S} > 1 $ -
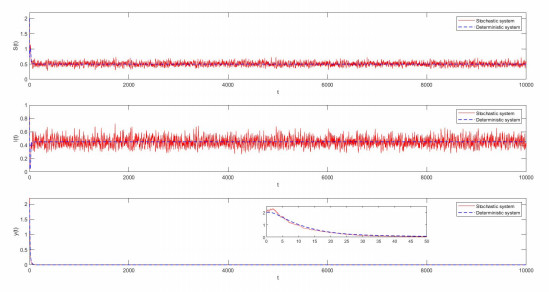
Figure 2.
The figure shows the solution of stochastic system and deterministic system when
$ r-\mu>\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{2} $ $ R_{p}^{S}<0 $ -
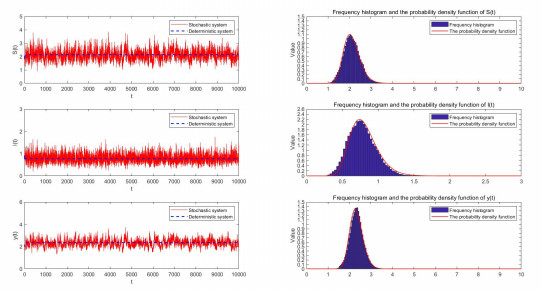
Figure 3.
The figure shows the solution of stochastic system and deterministic system when
$ r-\mu>\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{2} $ $ 0<R_{p}^{S}<1 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: