| Citation: | Shumin Zhou, Yunxian Dai, Hongyan Wang. STABILITY AND HOPF BIFURCATION ANALYSIS OF A NETWORKED SIR EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH TWO DELAYS AND DELAY DEPENDENT PARAMETERS[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(4): 1996-2026. doi: 10.11948/20240382 |
STABILITY AND HOPF BIFURCATION ANALYSIS OF A NETWORKED SIR EPIDEMIC MODEL WITH TWO DELAYS AND DELAY DEPENDENT PARAMETERS
-
Abstract
The spread of infectious diseases is generally influenced by the random contact of different individuals in uneven spatial structure. To describe this contact effect, network is introduced into a two delays SIR epidemic model with incubation period delay and temporary immunity delay. Due to the existence of the temporary immunity term, the characteristic equation of epidemic model has two delays and the parameters depend on one of them. We prove the stability of the disease-free equilibrium and the endemic equilibrium. We additionally obtain the stability switching curves to study the stability switching properties of the endemic equilibrium on the two delays plane when two delays change simultaneously, and further discuss the existence of Hopf bifurcation. The stability and the direction of the Hopf bifurcation are investigated with the normal form method and center manifold theorem. To illustrate our theoretical conclusions visually, we performed numerical simulation on a small-world Watts-Strogatz graph.
-

-
References
[1] Q. An, E. Beretta, Y. Kuang, C. C. Wang and H. Wang, Geometric stability switch criteria in delay differential equations with two delays and delay dependent parameters, J. Differ. Equ., 2019, 266(11), 7073–7100. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2018.11.025 [2] M. Barman and N. Mishra, Hopf bifurcation analysis for a delayed nonlinear-SEIR epidemic model on networks, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2024, 178, 114351. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.114351 [3] J. R. Beddington, Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency, J. Anim. Ecol., 1975, 44, 331–340. doi: 10.2307/3866 [4] E. Beretta and Y. Tang, Extension of a geometric stability switch criterion, Funkc Ekvacioj, 2003, 46(3), 337–361. doi: 10.1619/fesi.46.337 [5] C. J. Briggs and H. C. J. Godfray, The dynamics of insect-pathogen interactions in stage-structured populations, Am. Nat., 1995, 145(6), 855–887. doi: 10.1086/285774 [6] X. X. Cheng, Y. Wang and G. Huang, Global dynamics of a network-based SIQS epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate, Chaos Solitons Fractals., 2021, 153, 111502. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111502 [7] P. H. Crowley and E. K. Martin, Functional responses and interference within and between year classes of a dragonfly population, J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc., 1989, 8(3), 211–221. doi: 10.2307/1467324 [8] B. Dubey, P. Dubey and U. S. Dubey, Dynamics of an SIR model with nonlinear incidence and treatment rate, Appl. Appl. Math., 2015, 10(2), 5. [9] B. Dubey, A. Patra, P. K. Srivastava and U. S. Dubey, Modeling and analysis of an SEIR model with different types of nonlinear treatment rates, J. Biol. Syst., 2013, 21(03), 1350023. doi: 10.1142/S021833901350023X [10] P. Dubey, B. Dubey and U. S. Dubey, An SIR model with nonlinear incidence rate and Holling type III treatment rate, Applied Analysis in Biological and Physical Sciences: ICMBAA, Aligarh, India, June 2015. Springer India, 2016. [11] Y. Enatsu, Y. Nakata amd Y. Muroya, Global stability of SIRS epidemic models with a class of nonlinear incidence rates and distributed delays, Acta Math. Sci., 2012, 32(3), 851–865. doi: 10.1016/S0252-9602(12)60066-6 [12] S. J. Gao, L. S. Chen, J. J. Nieto and A. Torres, Analysis of a delayed epidemic model with pulse vaccination and saturation incidence, Vaccine., 2006, 24(35–36), 6037–6045. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.05.018 [13] K. Goel, A. Kumar and Nilam, A deterministic time-delayed SVIRS epidemic model with incidences and saturated treatment, J. Eng. Math., 2020, 121(1), 19–38. doi: 10.1007/s10665-020-10037-8 [14] K. Goel, A. Kumar and Nilam, Stability analysis of a logistic growth epidemic model with two explicit time-delays, the nonlinear incidence and treatment rates, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2022, 68(3), 1901–1928. doi: 10.1007/s12190-021-01601-1 [15] K. Goel and Nilam, A mathematical and numerical study of a SIR epidemic model with time delay, nonlinear incidence and treatment rates, Theory Biosci., 2019, 138(2), 203–213. doi: 10.1007/s12064-019-00275-5 [16] J. L. Herrera-Diestra, J. M. Buldu, M. Chavez and J. H. Martínez, Using symbolic networks to analyse dynamical properties of disease outbreaks, P. Roy. Soc. A-Math. Phy., 2020, 476(2236), 20190777. [17] H. W. Hethcote, The mathematics of infectious diseases, SIAM Rev., 2000, 42(4), 599–653. doi: 10.1137/S0036144500371907 [18] H. W. Hethcote and P. van den Driessche, Some epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence, J. Math. Biol., 1991, 29(3), 271–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00160539 [19] G. Huang, Y. Takeuchi, W. B. Ma and D. J. Wei, Global stability for delay SIR and SEIR epidemic models with nonlinear incidence rate, Bull. Math. Biol., 2010, 72, 1192–1207. doi: 10.1007/s11538-009-9487-6 [20] Z. C. Jiang and Y. F. Guo, Hopf bifurcation and stability crossing curve in a planktonic resource-consumer system with double delays, Int. J. Bifurcat Chaos, 2020, 30(13), 2050190. doi: 10.1142/S0218127420501904 [21] Z. C. Jiang and W. B. Ma, Permanence of a delayed SIR epidemic model with general nonlinear incidence rate, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci., 2015, 38(3), 505–516. doi: 10.1002/mma.3083 [22] W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick, A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics, Proc. R. Soc. Lond., 1927, 115(772), 700–721. [23] A. Kumar and Nilam, Stability of a time delayed SIR epidemic model along with nonlinear incidence rate and Holling type-II treatment rate, Int. J. Comput. Methods., 2018, 15(06), 1850055. doi: 10.1142/S021987621850055X [24] Y. N. Kyrychko and K. B. Blyuss, Global properties of a delayed SIR model with temporary immunity and nonlinear incidence rate, Nonlinear Anal. -Real World Appl., 2005, 6(3), 495–507. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2004.10.001 [25] S. Li, C. D. Huang and X. Y. Song, Detection of Hopf bifurcations induced by pregnancy and maturation delays in a spatial predator-prey model via crossing curves method, Chaos Solitons Fractals., 2023, 175, 114012. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.114012 [26] J. Liu, J. Chen and C. R. Tian, Stability of Turing bifurcation in a weighted networked reaction-diffusion system, Appl. Math. Lett., 2021, 118, 107135. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2021.107135 [27] W. M. Liu, S. A. Levin and Y. Iwasa, Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models, J. Math. Biol., 1986, 23, 187–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00276956 [28] Z. H. Liu and C. R. Tian, A weighted networked SIRS epidemic model, J. Differ. Equ., 2020, 269(12), 10995–11019. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2020.07.038 [29] W. Lv, H. F. He and K. Z. Li, Robust optimal control of a network-based SIVS epidemic model with time delay, Chaos Solitons Fractals., 2022, 161, 112378. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112378 [30] Y. Ma and Y. X. Dai, Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis of a fractional-order ring-hub structure neural network with delays under parameters delay feedback control, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2023, 20(11), 20093–20115. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023890 [31] C. R. Tian, Z. H. Liu and S. G. Ruan, Asymptotic and transient dynamics of SEIR epidemic models on weighted networks, Eue. J. Appl. Math., 2023, 34(2), 238–261. doi: 10.1017/S0956792522000109 [32] C. R. Tian, Q. Y. Zhang and L. Zhang, Global stability in a networked SIR epidemic model, Appl. Math. Lett., 2020, 107, 106444. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2020.106444 [33] D. H. Wang, Y. D. Liu, X. J. Gao, C. C. Wang and D. J. Fan, Dynamics of an HIV infection model with two time delays, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. -Ser. B, 2023, 28(11), 5641–5661. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2023069 [34] H. J. Wang, Y. H. Xu, M. Li and M. B. Hu, Impact of population size on epidemic spreading in a bipartite metapopulation network with recurrent mobility, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C, 2024, 35(08), 1–13. [35] J. H. Wang and Q. H. Jiang, Analysis of an SIS epidemic model with treatment, Adv. Differ. Equ., 2014, 1–10. [36] W. D. Wang, Backward bifurcation of an epidemic model with treatment, Math. Biosci., 2006, 201(1–2), 58–71. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2005.12.022 [37] W. D. Wang and S. G. Ruan, Bifurcations in an epidemic model with constant removal rate of the infectives, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 2004, 291(2), 775–793. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2003.11.043 [38] D. J. Watts and S. H. Strogatz, Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks, Nature, 1998, 393(6684), 440–442. doi: 10.1038/30918 [39] R. Xu and Z. E. Ma, Stability of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate, Chaos Solitons Fractals., 2009, 41(5), 2319–2325. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2008.09.007 [40] X. F. Xu and J. J. Wei, Bifurcation analysis of a spruce budworm model with diffusion and physiological structures, J. Differ. Equ., 2017, 262(10), 5206–5230. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2017.01.023 [41] X. P. Yuan, Y. K. Xue and M. X. Liu, Analysis of an epidemic model with awareness programs by media on complex networks, Chaos Solitons Fractals., 2013, 48, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2012.12.001 -
-
-
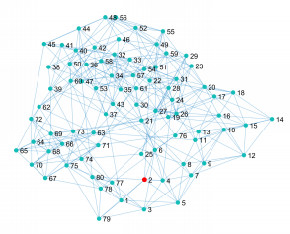
Figure 1.
Watts-Strogatz network WS(
$ m $ $ r $ $ p_1 $ -
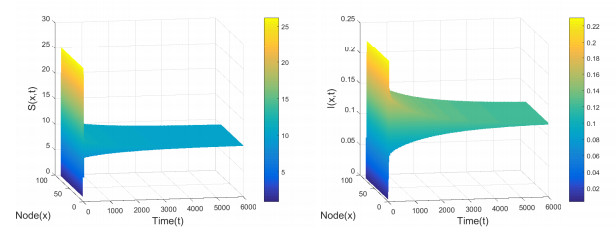
Figure 2.
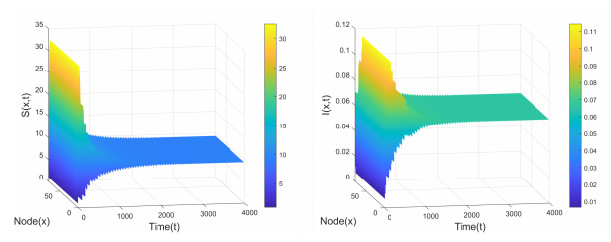
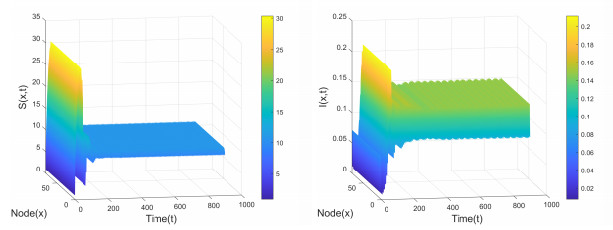
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(10.4348, 0.1517) $ $ \tau_1=0, \tau_2=0 $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
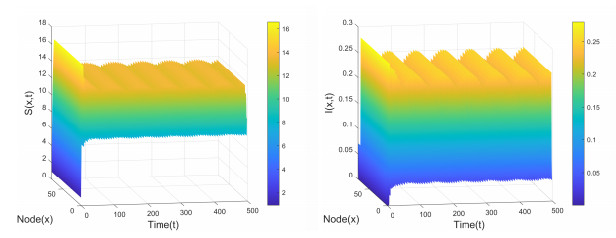
Figure 3.
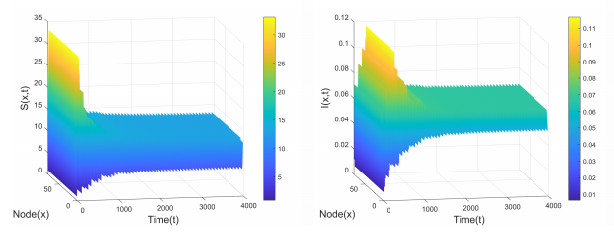
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(9.3356, 0.0658) $ $ \tau_1=\tau_2=15 $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
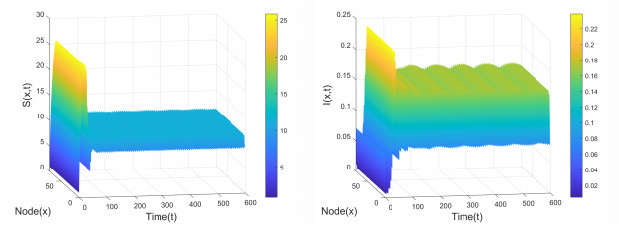
Figure 4.
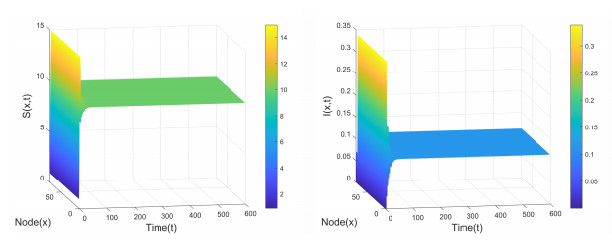
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(9.2648, 0.0602) $ $ \tau_1=\tau_2=19 $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
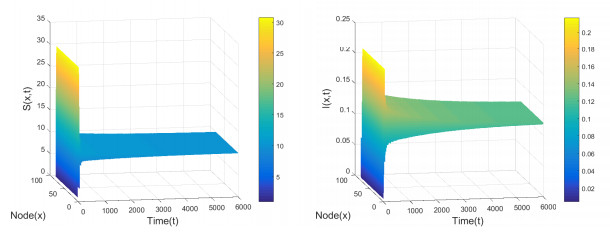
Figure 5.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(9.9372, 0.1128) $ $ \tau_1=0, \tau_2=3 $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
Figure 6.
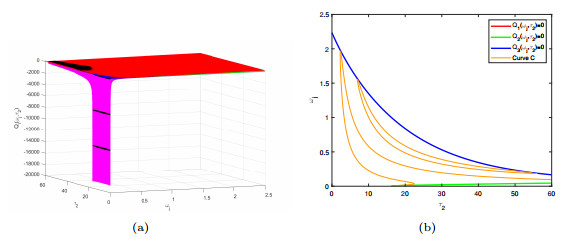
(a) The image of
$ Q_i(\omega_j, \tau_2) $ $ i=1, 2, 3 $ $ \omega_j\in (0, 2.5], \tau_2\in [0, 60] $ $ \Omega $ $ C $ -
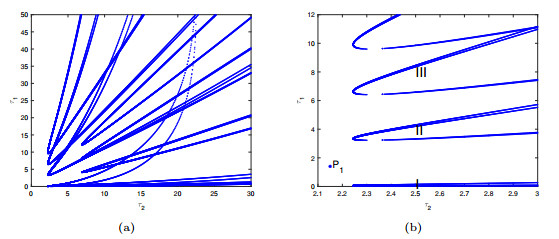
Figure 7.
(a) The stability switching curves
$ \mathcal{T} $ -
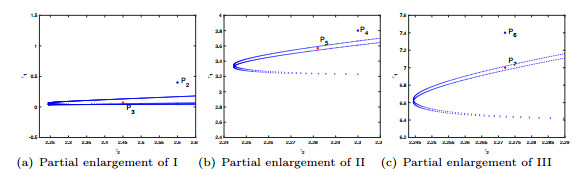
Figure 8.
Partial enlargements of Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ of Figure 6(b) and cross direction.
-
Figure 9.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2( 10.0438, 0.1211) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_1(1.4, 2.15) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
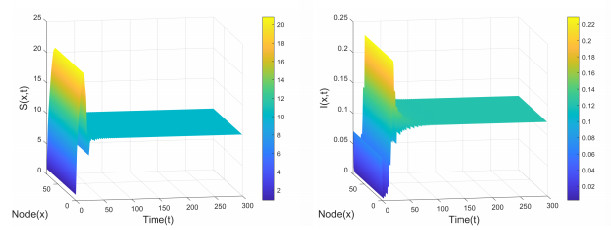
Figure 10.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2( 9.9849, 0.1165) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_2(0.4, 2.6) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
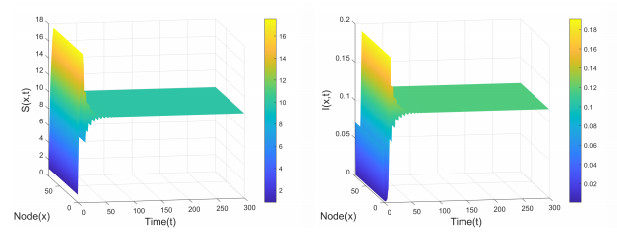
Figure 11.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2( 10.0039, 0.1180) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_3(0.07, 2.45) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
Figure 12.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(10.0235, 0.1195) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_4(3.8, 2.3) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
Figure 13.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(10.0259, 0.1197) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_5(3.57, 2.282) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
Figure 14.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(10.0272, 0.1198) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_6(7.4, 2.272) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $ -
Figure 15.
Positive equilibrium
$ E_2(10.0271, 0.1197) $ $ (\tau_1, \tau_2)=P_7(7, 2.272) $ $ (S_0, I_0)=(0.9114, 0.0710) $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: