| Citation: | Qianqian Li, Fengde Chen, Lijuan Chen, Zhong Li. DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF A DISCRETE AMENSALISM SYSTEM WITH THE BEDDINGTON-DEANGELIS FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE AND FEAR EFFECT[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(4): 2089-2123. doi: 10.11948/20240399 |
DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF A DISCRETE AMENSALISM SYSTEM WITH THE BEDDINGTON-DEANGELIS FUNCTIONAL RESPONSE AND FEAR EFFECT
-
Abstract
This paper proposes a discrete amensalism with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response response and fear effect on the first species. By comparison and study of different bifurcations, the introduction of the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response not only increased the dynamical behaviour of the system, including the emergence of pitchfork bifurcation and fold bifurcation, but also reduced the rate of extinction of the first species. Furthermore, we analyze the influence of the fear effect on the system, specifically focusing on the boundary equilibrium $E_2$ and the positive equilibrium $E_1^*$. Our findings reveal that when the second species is in a chaotic state, due to the persistence of the second species, the fear effect may have increased the stability of the first species or accelerated the extinction of the first species; when the second species is stable, the fear effect plays an essential part in maintaining the stability of the first species. Moreover, an appropriate fear effect promotes the coexistence of the first and second species. However, if the fear effect becomes excessively large, it directly results in the extinction of the first species. The discovery further enhances the understanding of the influence generated by amensalism through the fear effect.
-
Keywords:
- Amensalism /
- Beddington-DeAngelis functional response /
- fear effect /
- bifurcation /
- Chaos control
-

-
References
[1] R. Banerjee, P. Das and D. Mukherjee, Effects of fear and anti-predator response in a discrete system with delay, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2022, 27(7), 3643–3661. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2021200 [2] J. R. Beddington, Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency, J. Anim. Ecol., 1975, 44, 331–340. doi: 10.2307/3866 [3] F. Chen, M. Zhang and R. Han, Existence of positive periodic solution of a discrete Lotka-Volterra amensalism model, J. Shengyang Univ. (Nat. Sci. ), 2015, 27(3), 251–254. [4] J. Chen, X. He and F. Chen, The influence of fear effect to a discrete-time predator-prey system with predator has other food resource, Mathematics, 2021, 9(8), 865. doi: 10.3390/math9080865 [5] S. Chen, F. Chen, V. Srivastava and R. D. Parshad, Dynamical analysis of an allelopathic phytoplankton model with fear effect, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2024, 23(4), 189. doi: 10.1007/s12346-024-01047-3 [6] J. Danane, M. Yavuz and M. Yıldız, Stochastic modeling of three-species prey-predator model driven by Lévy jump with mixed Holling-II and Beddington-DeAngelis functional responses, Fractal and Fractional, 2023, 7(10), 751. doi: 10.3390/fractalfract7100751 [7] D. L. DeAngelis, R. A. Goldstein and R. V. O'neill, A model for tropic interaction, Ecology, 1975, 56(4), 881–892. doi: 10.2307/1936298 [8] Q. Din, Dynamics and chaos control for a novel model incorporating plant quality index and larch budmoth interaction, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2021, 153, 111595. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111595 [9] Q. Din, K. Jameel and M. S. Shabbir, Discrete-time predator-prey system incorporating fear effect: Stability, bifurcation, and chaos control, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2024, 23(1), 1–43. doi: 10.1007/s12346-023-00858-0 [10] Q. Din and M. I. Khan, A discrete-time model for consumer-resource interaction with stability, bifurcation and chaos control, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2021, 20(2), 56. doi: 10.1007/s12346-021-00488-4 [11] Q. Din, R. A. Naseem and M. S. Shabbir, Predator-prey interaction with fear effects: Stability, bifurcation and two-parameter analysis incorporating complex and fractal behavior, Fractal and Fractional, 2024, 8(4), 221. doi: 10.3390/fractalfract8040221 [12] Q. Din and M. A. Zulfiqar, Qualitative behavior of a discrete predator-prey system under fear effects, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 2022, 77(11), 1023–1043. doi: 10.1515/zna-2022-0129 [13] Y. Dong, D. Wu and C. Shen, Influence of fear effect and predator-taxis sensitivity on dynamical behavior of a predator-prey model, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 2022, 73(1), 25. doi: 10.1007/s00033-021-01659-8 [14] K. H. Elliott, G. S. Betini and D. R. Norris, Experimental evidence for within-and cross-seasona effects of fear on survival and reproduction, J. Anim. Ecol., 2016, 85(2), 507–515. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.12487 [15] C. C. García and J. V. Cuenca, Additive Allee effect on prey in the dynamics of a Gause predator-prey model with constant or proportional refuge on prey at low or high densities, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2023, 126, 107427. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2023.107427 [16] C. García, M. Rendueles and M. Díaz, Microbial amensalism in Lactobacillus casei and Pseudomonas taetrolens mixed culture, Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng., 2017, 40, 1111–1122. doi: 10.1007/s00449-017-1773-3 [17] J. M. Gómez and A. González-Megías, Asymmetrical interactions between ungulates and phytophagous insects: Being different matters, Ecology, 2002, 83(1), 203–211. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0203:AIBUAP]2.0.CO;2 [18] X. Guan and F. Chen, Dynamical analysis of a two species amensalism model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and Allee effect on the second species, Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 2019, 48, 71–93. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2019.01.002 [19] X. Guan and H. Deng, The qualitative analysis of a two species amesnalism model with non-monotonic functional response and Allee effect on second species, Ann. of Appl. Math., 2019, 35(2), 126–138. [20] W. Ishaque, Q. Din, K. A. Khan, et al., Dynamics of predator-prey model based on fear effect with bifurcation analysis and chaos control, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2024, 23(1), 26. doi: 10.1007/s12346-023-00878-w [21] H. Jiang and T. D. Rogers, The discrete dynamics of symmetric competition in the plane, J. Math. Biol., 1978, 25(6), 573–596. [22] K. Kundu, S. Pal, S. Samanta, et al., Impact of fear effect in a discrete-time predator-prey system, Bull. Calcutta Math. Soc., 2018, 110, 245–264. [23] C. Lei, Dynamic behaviors of a stage structure amensalism system with a cover for the first species, Adv. Differ. Equations, 2018, 2018, 1–23. doi: 10.1186/s13662-017-1452-3 [24] L. Li, Z. Hou and Y. Mao, Dynamical transition and bifurcation of a diffusive predator-prey model with an Allee effect on prey, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 2023, 126, 107433. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2023.107433 [25] Q. Li, A. J. Kashyap, Q. Zhu, et al., Dynamical behaviours of discrete amensalism system with fear effects on first species, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 21(1), 832–860. [26] Q. Lin and X. Zhou, On the existence of positive periodic solution of an amensalism model with Holling Ⅱ functional response, Math. Biol. Neurosci., 2017, 2017, Article ID 3. [27] H. Liu, H. Yu, C. Dai, et al., Dynamical analysis of an aquatic amensalism model with non-selective harvesting and Allee effect, Math. Biosci. Eng., 2021, 18(6), 8857–8882. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021437 [28] J. Liu, B. Liu, P. Lv and T. Zhang, An eco-epidemiological model with fear effect and hunting cooperation, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2021, 142, 110494. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110494 [29] Y. Liu, L. Zhao and X. Huang, Stability and bifurcation analysis of two species amensalism model with Michaelis-Menten type harvesting and a cover for the first species, Adv. Differ. Equations, 2018, 2018, 1–19. doi: 10.1186/s13662-017-1452-3 [30] D. Luo and Q. Wang, Global dynamics of a Beddington-DeAngelis amensalism system with weak Allee effect on the first species, Appl. Math. Comput., 2021, 408, 126368. [31] D. Luo and Q. Wang, Global dynamics of a Holling-II amensalism system with nonlinear growth rate and Allee effect on the first species, Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos, 2021, 31(03), 2150050. doi: 10.1142/S0218127421500504 [32] X. Luo, G. Chen, B. Wang and J. Fang, Hybrid control of period-doubling bifurcation and chaos in discrete nonlinear dynamical systems, Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2003, 18, 775–783. doi: 10.1016/S0960-0779(03)00028-6 [33] J. C. Maerz, N. L. Panebianco and D. M. Madison, Effects of predator chemical cues and behavioral biorhythms on foraging, activity of terrestrial salamanders, J. Chem. Ecol., 2001, 27(7), 1333–1344. doi: 10.1023/A:1010309108210 [34] B. T. Mulugeta, L. Yu and Q. Yuan, Bifurcation analysis of a predator-prey model with strong Allee effect and Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2023, 28(3), 1938–1963. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2022153 [35] D. L. Ogada, M. E. Gadd and R. S. Ostfeld, Impacts of large herbivorous mammals on bird diversity and abundance in an African savanna, Oecologia. 2008, 156, 387–397. doi: 10.1007/s00442-008-0994-1 [36] K. Sarkar and S. Khajanchi, Impact of fear effect on the growth of prey in a predator-prey interaction model, Ecol. Complexity, 2020, 42, 100826. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2020.100826 [37] G. T. Skalski and J. F. Gilliam, Functional responses with predator interference: Viable alternatives to the Holling type II model, Ecology, 2001, 82(11), 3083–3092. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[3083:FRWPIV]2.0.CO;2 [38] G. Sun, Qualitative analysis on two populations amensalism model, J. Jiamusi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. ), 2003, 21(3), 283–286. [39] M. S. Surendar, M. Sambath and K. Balachandran, Qualitative analysis of a prey-predator model with prey refuge and intraspecific competition among predators, Boundary Value Probl., 2023, 2023(1), 81. doi: 10.1186/s13661-023-01771-w [40] X. Wang, L. Zanette and X. Zou, Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions, J. Math. Biol., 2016, 73(5), 1179–1204. doi: 10.1007/s00285-016-0989-1 [41] Z. Wei, Y. Xia and T. Zhang, Stability and bifurcation analysis of an amensalism model with weak Allee effect, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2020, 19, 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s12346-019-00337-5 [42] R. Wu, A two species amensalism model with non-monotonic functional response, Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci., 2016, 2016, Article ID 19. [43] R. Wu, L. Zhao and Q. Lin, Stability analysis of a two species amensalism model with Holling II functional response and a cover for the first species, J. Nonlinear Funct. Anal., 2016, 2016, 46. [44] X. Xi, J. N. Griffin and S. Sun, Grasshoppers amensalistically suppress caterpillar performance and enhance plant biomass in an alpine meadow, Oikos, 2013, 122(7), 1049–1057. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0706.2012.00126.x [45] X. Xie, F. Chen and M. He, Dynamic behaviors of two species amensalism model with a cover for the first species, J. Math. Comput. Sci., 2016, 16(2), 395–401. [46] P. Xue and C. Ren, Spatial patterns for a predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and fractional cross-diffusion, AIMS Math., 2023, 8(8), 19413–19426. doi: 10.3934/math.2023990 [47] L. Y. Zanette, A. F. White and M. C. Allen, Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per yea, Science, 2011, 334, 1398–1401. doi: 10.1126/science.1210908 [48] M. Zhao and Y. Du, Stability and bifurcation analysis of an amensalism system with Allee effect, Adv. Differ. Equations, 2020, 2020, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13662-019-2438-0 [49] Q. Zhou and F. Chen, Dynamical analysis of a discrete amensalism system with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and Allee effect for the unaffected species, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2023, 22(1), 16. doi: 10.1007/s12346-022-00716-5 [50] Q. Zhou, F. Chen and S. Lin, Complex dynamics analysis of a discrete amensalism system with a cover for the first species, Axioms, 2022, 11(8), 365. doi: 10.3390/axioms11080365 [51] Q. Zhu, F. Chen, Z. Li and L. Chen, Global dynamics of two-species amensalism model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and fear effect, Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos, 2024, 34(06), 2450075. doi: 10.1142/S0218127424500755 -
-
-
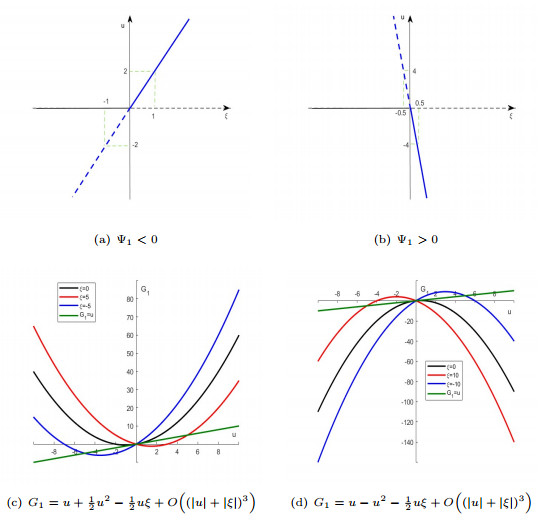
Figure 1.
Flip bifurcation image of system (1.7) at
$ E_2(0, \gamma) $ $ \alpha=6 $ $ c=1 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ \beta=1 $ $ k=1$ -
Figure 2.
The transcritical bifurcation diagram of system (1.7) at
$ E_2 $ $ \alpha=4 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ k=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ c=2 $ $ \beta=0.25 $ $ \alpha=4 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ k=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ c=2 $ $ \beta=1.5 $ -
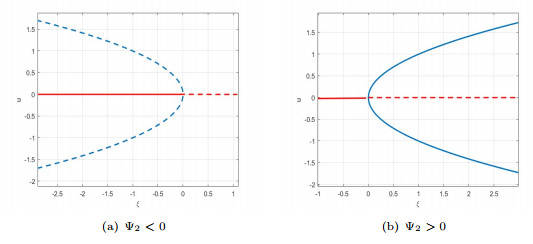
Figure 3.
The pitchfork bifurcation diagram of system (1.7) at
$ E_2 $ $ \alpha=4 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ k=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ c=2 $ $ \beta=1 $ $ \alpha=4 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ k=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ c=2 $ $ \beta=2 $ -
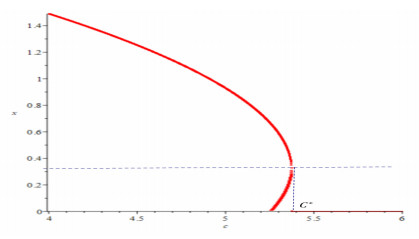
Figure 4.
The fold bifurcation diagram of system (1.7) at
$ E_3^*(x_3^*, \gamma) $ $ c=c^*=5.37 $ $ \alpha=4 $ $ \beta=1 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ k=0.1 $ -
Figure 5.
Flip bifurcation diagram of system (1.7) at
$ E_1^*(x_1^*, \gamma) $ $ \alpha=5 $ $ c=1 $ $ k=0.1 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ -
Figure 6.
Diagrams of bifurcation for controlled system (5.2).
-
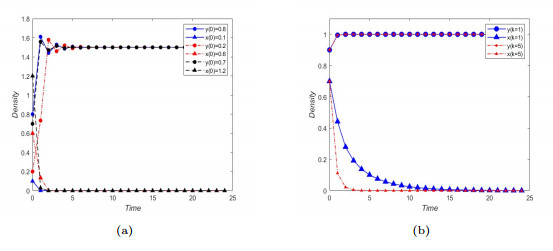
Figure 7.
(a) Global stability of
$ E_1 $ $ \alpha=2.1 $ $ \delta $ $ c=11 $ $ \beta=1 $ $ \gamma=0.5 $ $ E_1 $ $ k=1 $ $ k=5 $ -
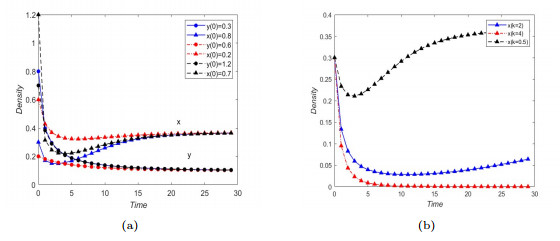
Figure 8.
(a) Global stability of
$ E_1^* $ $ \alpha=2 $ $ \delta $ $ c=0.5 $ $ \beta=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $ $ x $ $ k=0.5 $ $ k=2 $ $ k=4 $ -
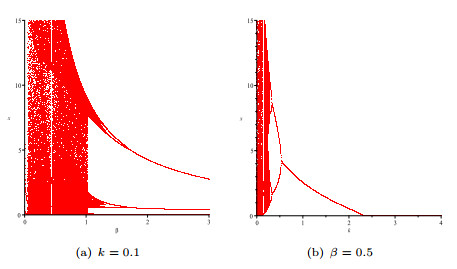
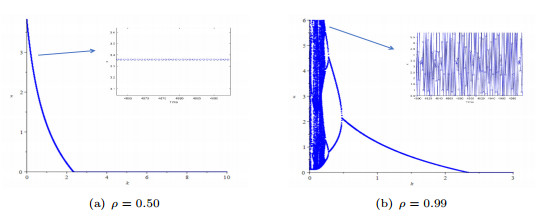
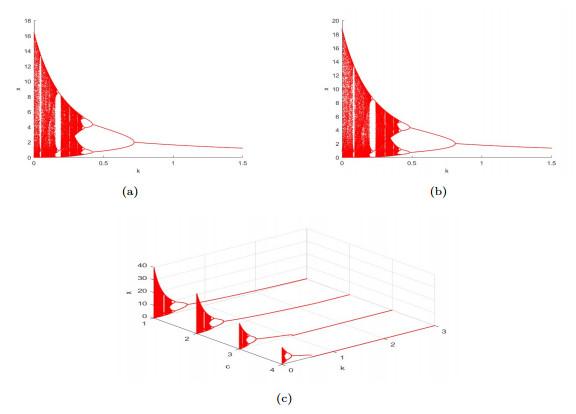
Figure 9.
The bifurcation plot of
$ x $ $ k $ -
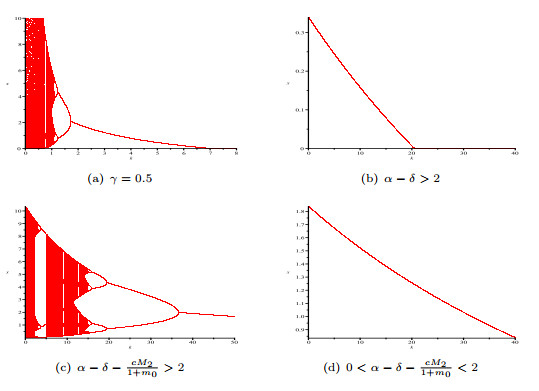
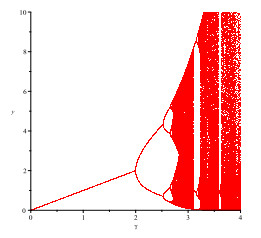
Figure 10.
(a) represent bifurcation plot of system (1.4) with
$ e_1=4.3 $ $ e_2=0.3 $ $ a_2=1 $ $ c=0.2 $ $ \alpha=5 $ $ \beta=0.5 $ $ c=1 $ $ \delta=1 $ $ \gamma=1 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: