| Citation: | Fuchen Zhang, Song Chen, Xiusu Chen, Fei Xu, Min Xiao. QUALITATIVE BEHAVIORS AND CONTROL OF A NEW FOUR-DIMENSIONAL LORENZ SYSTEM[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis & Computation, 2025, 15(5): 3025-3044. doi: 10.11948/20240462 |
QUALITATIVE BEHAVIORS AND CONTROL OF A NEW FOUR-DIMENSIONAL LORENZ SYSTEM
-
Abstract
In this paper, a new nonlinear four-dimensional Lorenz system is proposed. Nonlinear dynamical properties of this system, including the stability of the fixed points, Lyapunov exponents, the bifurcation behaviors and sensitivity to initial conditions, are considered by using chaos theory and numerical simulations. It is very interesting that we find that this system exhibits chaos phenomena for a set of parameters. The globally exponential attractive set of this system has been obtained according to Lyapunov stability theory. Synchronization has been realized between two identical hyperchaotic systems via globally exponential approach and sliding mode control method by using the results of the global exponential attractive set, Vaidyanathan's theorem and Dini derivative. The novelty of the paper lies in that the globally exponential attractive set of the system is obtained firstly, then the result of the globally exponential attractive set is used to study chaos control and chaos synchronization. Furthermore, the precise mathematical expression of the controller is obtained according to the boundedness of this system. Finally, the synchronization process is simulated by MATLAB to illustrate the effectiveness of the theoretical analysis. The results of numerical simulations show that two control methods for chaos synchronization are effective.
-
Keywords:
- Lorenz system /
- stability theory /
- qualitative theory /
- bifurcation behavior /
- sliding mode control
-

-
References
[1] M. P. Asir, K. Thamilmaran, A. Prasad, U. Feudel, N. V. Kuznetsov and M. D. Shrimali, Hidden strange nonchaotic dynamics in a non-autonomous model, Chaos Soliton. Fract., 2023, 168, 113101. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113101 [2] T. L. Carroll and L. M. Pecora, Synchronizing chaotic circuits, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst., 1991, 38(4), 453–456. doi: 10.1109/31.75404 [3] G. Chen and T. Ueta, Yet another chaotic attractor, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 1999, 9, 1465–1466. doi: 10.1142/S0218127499001024 [4] L. Chua, M. Komuro and T. Matsumoto, The double scroll family, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst., 1986, 33(11), 1072–1118. doi: 10.1109/TCS.1986.1085869 [5] P. Frederickson, J. Kaplan, E. Yorke and J. Yorke, The Lyapunov dimension of strange attractors, J. Differ. Equ., 1983, 49(2), 185–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-0396(83)90011-6 [6] H. Fujisaka and T. Yamada, Stability theory of synchronized motion in coupled-oscillator systems, Prog. Theor. Phys., 1983, 69(1), 32–47. doi: 10.1143/PTP.69.32 [7] W. W. Ho and S. Choi, Exact emergent quantum state designs from quantum chaotic dynamics, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2022, 128(6), 060601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.060601 [8] Y. Y. Huang, H. J. Huang, Y. C. Huang, Y. H. Wang, F. Yu and B. Yu, Drive-response asymptotic shape synchronization for a class of two-dimensional chaotic systems and its application in image encryption, Physica D., 2024, 463, 134162. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2024.134162 [9] D. Khattar, N. Agrawal and G. Singh, Chaos synchronization of a new chaotic system having exponential term via adaptive and sliding mode control, Differ. Equ. Dyn. Syst., 2023, 1–19. https//doi. org/10.1007/s12591-023-00635-0. doi: 10.1007/s12591-023-00635-0 [10] J. S. Kim, D. H. Kim, J. H. Lee and J. S. Lee, Smooth pulse number transition strategy considering time delay in synchronized SVPWM, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 2022, 38(2), 2252–2261. [11] N. Kuznetsov, T. Mokaev, O. Kuznetsova and E. V. Kudryashova, The Lorenz system: Hidden bounary of practical stability and the Lyapunov dimension, Nonlinear Dyn., 2020, 102, 713–732. doi: 10.1007/s11071-020-05856-4 [12] N. Kuznetsov, T. Mokaev, V. Ponomarenko, E. Seleznev, N. Stankevich and L. Chua, Hidden attractors in Chua circuit: Mathematical theory meets physical experiments, Nonlinear Dyn., 2023, 111(6), 5859–5887. doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-08078-y [13] G. Laarem, A new 4-D hyper chaotic system generated from the 3-D Rosslor chaotic system, dynamical analysis, chaos stabilization via an optimized linear feedback control, it's fractional order model and chaos synchronization using optimized fractional order sliding mode control, Chaos Soliton. Fract., 2021, 152, 111437. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111437 [14] G. A. Leonov and V. A. Boichenko, Lyapunov's direct method in the estimation of the Hausdorff dimension of attractors, Acta Appl. Math., 1992, 26(1), 1–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00046607 [15] T. Y. Li and J. A. Yorke, Period three implies chaos, Am. Math. Mon., 1975, 82, 985–992. doi: 10.1080/00029890.1975.11994008 [16] M. Liu, J. Liu, J. Liang, Y. Sun and Y. Shu, Observer-based secure synchronization control of directed complex-valued dynamical networks under link attacks, Nonlinear Dyn., 2024, 112, 12303–12318. doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-09695-5 [17] E. N. Lorenz, Deterministic nonperiodic flow, J. Atmos. Sci., 1963, 20, 130–141. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2 [18] J. Lu and G. Chen, A new chaotic attractor coined, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 2002, 12(3), 659–661. doi: 10.1142/S0218127402004620 [19] J. Lu, G. Chen, D. Cheng and S. Celikovsky, Bridge the gap between the Lorenz system and the Chen system, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos., 2002, 12(12), 2917–2926. doi: 10.1142/S021812740200631X [20] G. M. Mahmoud, M. A. Al-Kashif and A. A. Farghaly, Chaotic and hyperchaotic attractors of a complex nonlinear system, J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 2008, 41(5), 055104. doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/41/5/055104 [21] M. Mohadeszadeh and N. Pariz, An application of adaptive synchronization of uncertain chaotic system in secure communication systems, Int. J. Simul. Model., 2022, 42(1), 143–152. doi: 10.1080/02286203.2020.1848281 [22] E. Nijholt, T. Pereira, F. C. Queiroz and D. Turaev, Chaotic behavior in diffusively coupled systems, Communications in Mathematical Physics, 2023, 401(3), 2715–2756. doi: 10.1007/s00220-023-04699-5 [23] H. Nijmeijer, A dynamical control view on synchronization, Physica D., 2001, 154(3–4), 219–228. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(01)00251-2 [24] A. Y. Pogromsky, G. Santoboni and H. Nijmeijer, An ultimate bound on the trajectories of the Lorenz system and its applications, Nonlinearity, 2003, 16, 1597–1605. doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/16/5/303 [25] H. Poincar$\acute{e}$, Sur le probleme des trois corps et les equations de la dynamique, Acta Math., 1890, 13, 1–270. [26] M. G. Rosenblum, A. S. Pikovsky and J. Kurths, Phase synchronization in driven and coupled chaotic oscillators, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst., 1997, 44(10), 874–881. doi: 10.1109/81.633876 [27] O. E. Rossler, An equation for continuous chaos, Phys. Lett. A, 1976, 57, 397–398. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(76)90101-8 [28] S. C. Sinha, J. T. Henrichs and B. Ravindra, A general approach in the design of active controllers for nonlinear systems exhibiting chaos, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 2000, 10(1), 165–178. doi: 10.1142/S0218127400000104 [29] C. Sparrow, The Lorenz Equations: Bifurcations, Chaos and Strange Attractors, Applied Mathematical Science, vol. 41, Springer, New York, 1982. [30] L. Stenflo, Generalized Lorenz equations for acoustic-gravity waves in the atmosphere, Phys. Scr., 1996, 3, 83–84. [31] S. Vaidyanathan, Global chaos synchronization of identical Li-Wu chaotic systems via sliding mode control, Int. J. Model. Identif. Control, 2014, 22(2), 170–177. doi: 10.1504/IJMIC.2014.064295 [32] S. Vaidyanathan, S. Sampath and A. T. Azar, Global chaos synchronisation of identical chaotic systems via novel sliding mode control method and its application to Zhu system, Int. J. Model. Identif. Control, 2015, 23(1), 92–100. doi: 10.1504/IJMIC.2015.067495 [33] J. C. Vallejo and M. A. Sanjuan, Predictability of Chaotic Dynamics, A Finite-time Lyapunov Exponents Approach, Springer, Cham, 2019. [34] A. Wagemakers, A. Hartikainen, A. Daza, E Rasanen and M. A. Sanjuan, Chaotic dynamics creates and destroys branched flow, Phys. Rev. E, 2025, 111(1), 014214. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.111.014214 [35] A. Wolf, J. B. Swift, H. L. Swinney and J. A. Vastano, Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series, Physica D., 1985, 16, 285–317. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(85)90011-9 [36] F. C. Zhang, X. F. Liao, C. L. Mu, G. Y. Zhang and Y. Chen, On global boundedness of the Chen system, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B., 2017, 22(4), 1673–1681. [37] F. C. Zhang, X. F. Liao and G. Y. Zhang, Some new results for the generalized Lorenz system, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2017, 16(3), 749–759. doi: 10.1007/s12346-016-0206-z [38] F. C. Zhang, X. F. Liao, G. Y. Zhang and C. L. Mu, Dynamical analysis of the generalized Lorenz systems, J. Dyn. Control Syst., 2017, 23(2), 349–362. doi: 10.1007/s10883-016-9325-8 [39] F. C. Zhang, C. L. Mu, S. M. Zhou and P. Zheng, New results of the ultimate bound on the trajectories of the family of the Lorenz systems, Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B, 2015, 20(4), 1261–1276. doi: 10.3934/dcdsb.2015.20.1261 [40] F. C. Zhang and F. Xu, Dynamical behavior of the generzlized complex Lorenz chaotic system, J. Appl. Anal. Comp., 2024, 14(4), 1915–1931. [41] F. C. Zhang, F. Xu and X. Zhang, Qualitative behaviors of a four-dimensional Lorenz system, J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 2024, 57(9), 095201. [42] F. C. Zhang and G. Y. Zhang, Further results on ultimate bound on the trajectories of the Lorenz system, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., 2016, 15(1), 221–235. [43] F. C. Zhang, P. Zhou and F. Xu, Qualitative properties of a physically extended six-dimensional Lorenz system, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 2024, 34(7), 2450083. [44] X. Zhao, J. Liu, G. Chen, L. Chai and D. Wang, Dynamics and synchronization of complex-valued ring networks, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 2022, 32(5), 2230011. [45] S. Zhou, Y. C. Lai and W. Lin, Stochastically adaptive control and synchronization: From globally one-sided Lipschitzian to only locally Lipschitzian systems, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst., 2022, 21(2), 932–959. -
-
-
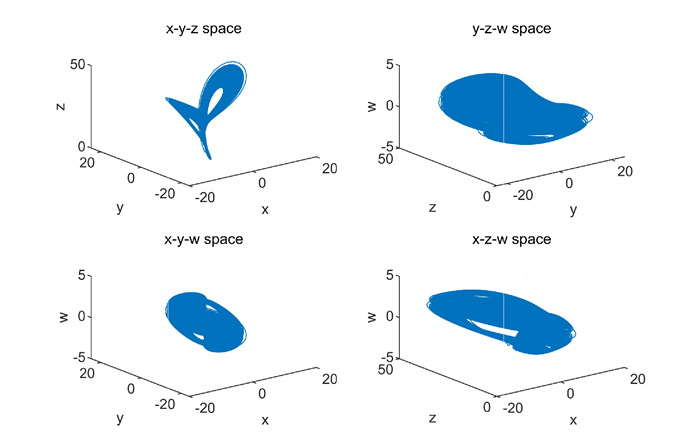
Figure 1.
The hyperchaotic attractors of system (2.1) in the 3D space.
-
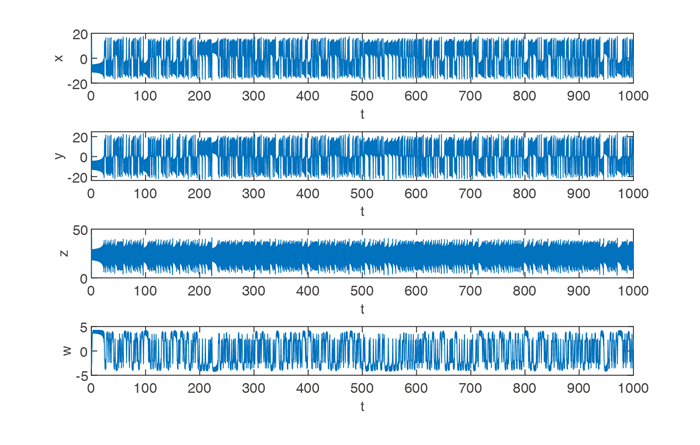
Figure 2.
The evolution process of each variable of system (2.1) over the time t.
-
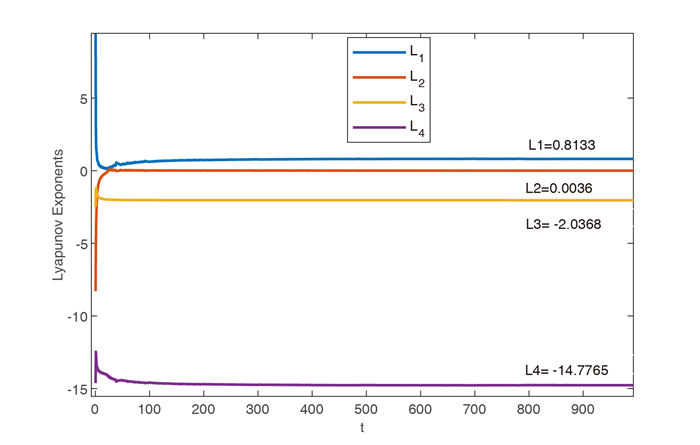
Figure 3.
The Lyapunov exponent chart of system (2.1).
-
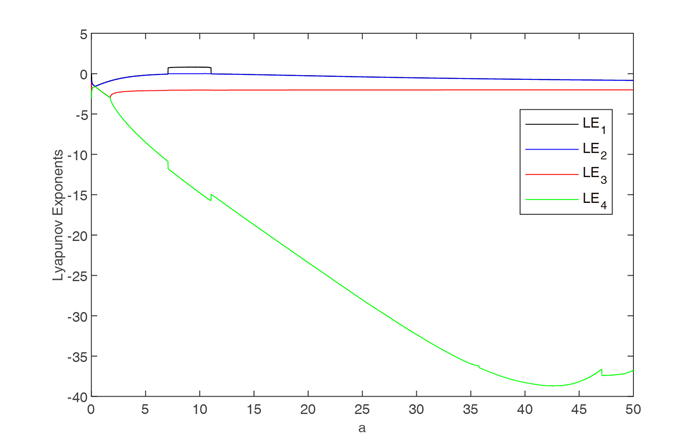
Figure 4.
Lyapunov exponents diagram of system (2.1) with
$ a \in [0,50] $ -
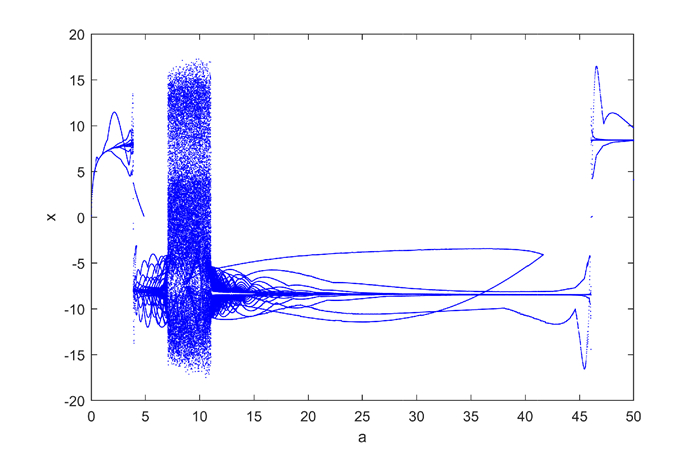
Figure 5.
Bifurcation diagram of state variable
$ x $ $ a $ -
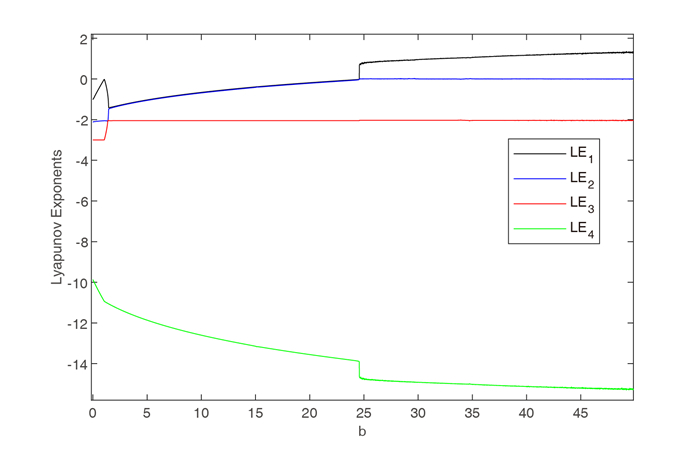
Figure 6.
Lyapunov exponents diagram of system (2.1) with
$ b \in [0,50] $ -
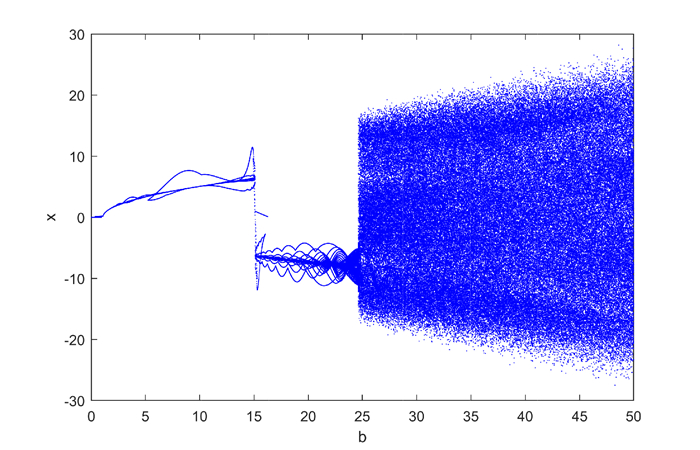
Figure 7.
Bifurcation diagram of state variable
$ x $ $ b $ -
Figure 8.
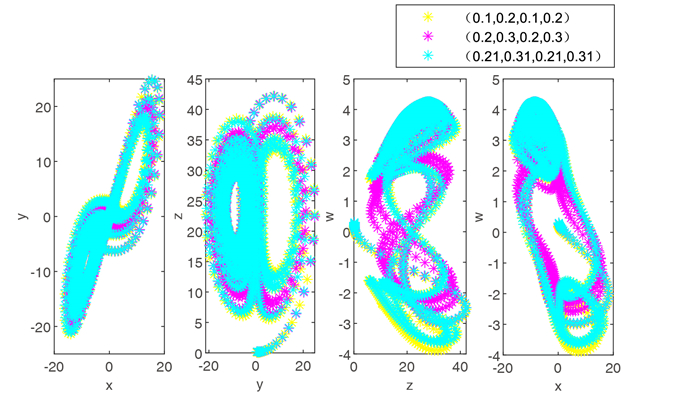
Initial value sensitivity map of system (2.1).
-
Figure 9.
Synchronization of linear feedback control for
$ {k_1} = 10,{k_2} = 53,{k_3} = 6350,{k_4} = 2 $ -
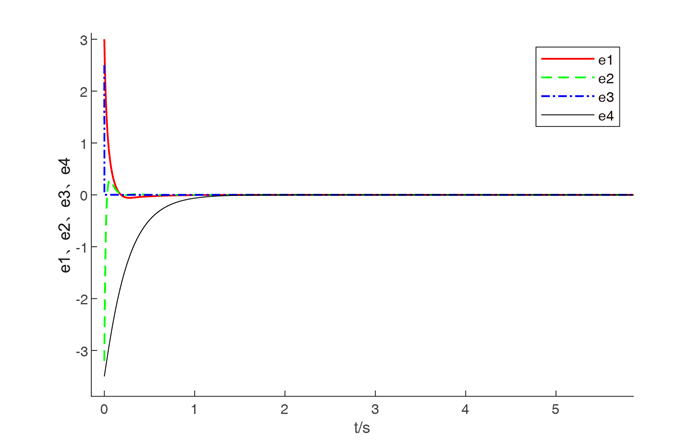
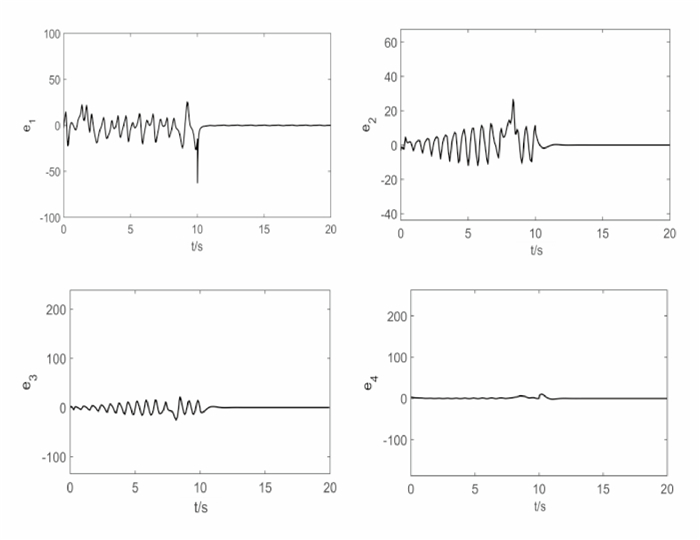
Figure 10.
Synchronization of sliding mode control is illustrated when
$ k=10,q=10 $




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: